/Dorsalpedisartery-23c28539f764403ca9254e32551049ce.jpg)
Dorsalis Pedis Artery Anatomy, Function, and Significance
Details of the image 'Normal foot x-rays' Modality: X-ray (Lateral)

Basketball Player With Left Foot Pain
This is a repository of radiograph examples (X-rays) of the pediatric (children) skeleton by age, from birth to 15 years. Ages are approximate (generally, at most +/- 1-2 months, but mostly within + / - 15 days - unless stated otherwise). Male and female subjects are intermixed. These normal bone xrays are NOT intended as bone-age references!
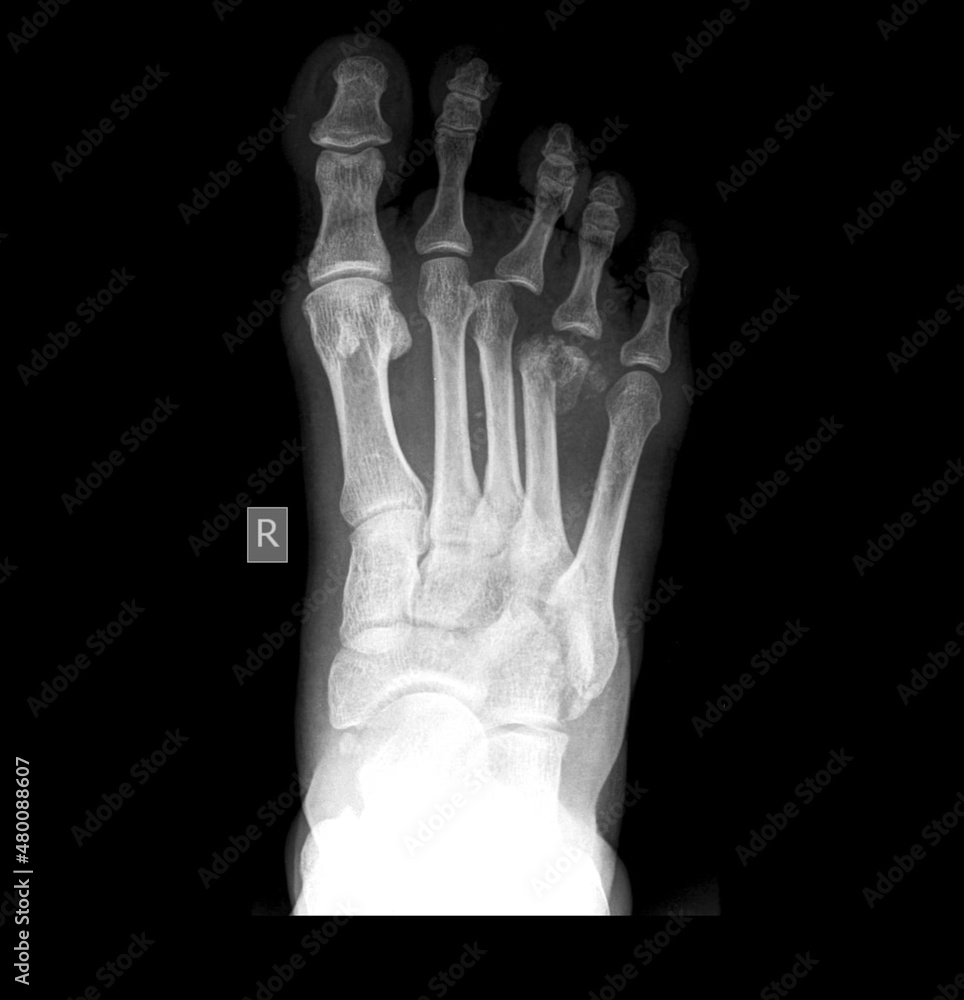
x ray image of fractures and dislocation of phalanx proximal pedis foto
It is useful in diagnosing fractures, soft tissue effusions, joint space abnormalities and localizing foreign bodies in pediatric patients. Patient position the patient is supine with the affected knee flexed plantar aspect of affected foot resting on the image receptor Technical factors anteroposterior projection centering point

Blood Supply to the Foot Foot & Ankle Orthobullets
Sesamoids and accessory ossicles seen in the foot vary widely in their prevalence and appearance. Occasionally, these bones may be associated with painful syndromes, due to various pathologies, including trauma, infection, inflammation, degeneration and others. However, symptomatic accessory and sesamoid bones are rare, and search for additional pathology should be performed. Although the.

Стоковая фотография 1459919189 Pedis X Ray Anatomy Radiology
A right foot X-ray was also performed, and similar findings were reported, although the athlete had no pain.. Os vesalianum pedis was first illustrated in the 16th century and named after its illustrator,. integrating the clinical and radiographic findings as well as knowledge of the accessory ossicle anatomy is mandatory to avoid.

Pedis X Ray Anatomy Radiology Radiographic Stock Photo 1459919165
Musculotendinous Extensor tendons attach on the dorsal aspect of the foot. In the great toe, the distal phalanx receives extensor hallucis longus whereas the proximal phalanx receives extensor hallucis brevis (part of extensor digitorum brevis ). An extensor expansion also exists, formed from extensor digitorum, the lumbricals and interossei.
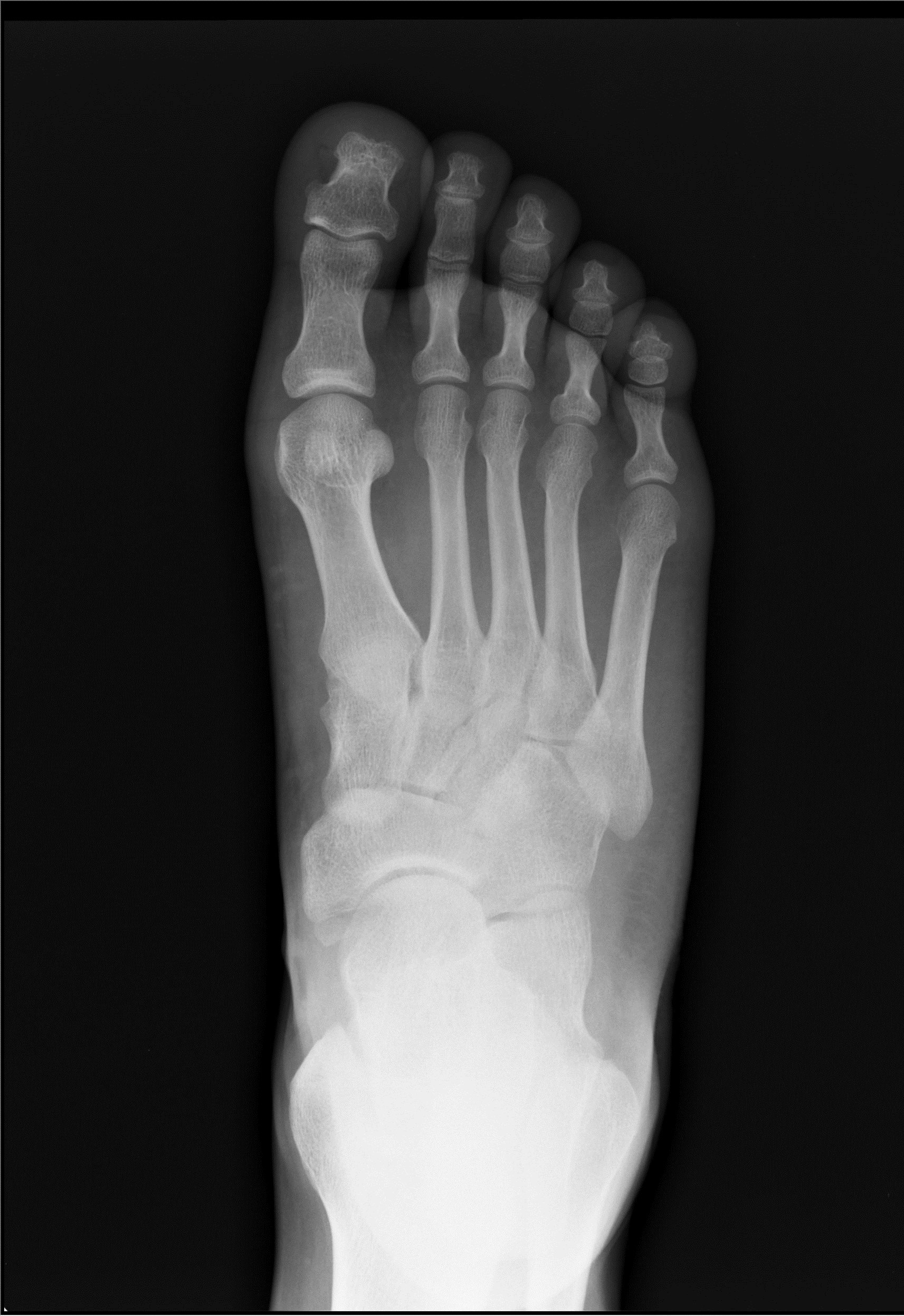
Podiatrist in Lehi Hallux Rigidus in Lehi Arches Foot and Ankle Clinic
Indications This projection is useful in diagnosing fractures; particularly 5 th metatarsal fractures, soft tissue effusions, joint space abnormalities and localizing foreign bodies in pediatric patients. Patient position the patient is supine with the affected knee flexed plantar aspect of the affected foot resting on the image receptor

Foot Oblique. Unidad Especializada en Ortopedia y Traumatologia www
Weight-bearing foot and ankle X-rays are used to evaluate the extent of navicular fragmentation, deformity, and arthritic changes [7,19-22]. Weight-bearing X-rays are also beneficial for ruling out navicular bone stress fractures and differentiating MWD from talonavicular (TN) joint arthritic changes caused by rheumatoid disease or previous trauma [ 19 - 21 ].

Foot Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Radiology student
Os vesalianum pedis is a rare accessory foot ossicle. It is usually asymptomatic, however, it can be an infrequent cause of lateral foot pain. We present the case of a 19-year-old healthy male.
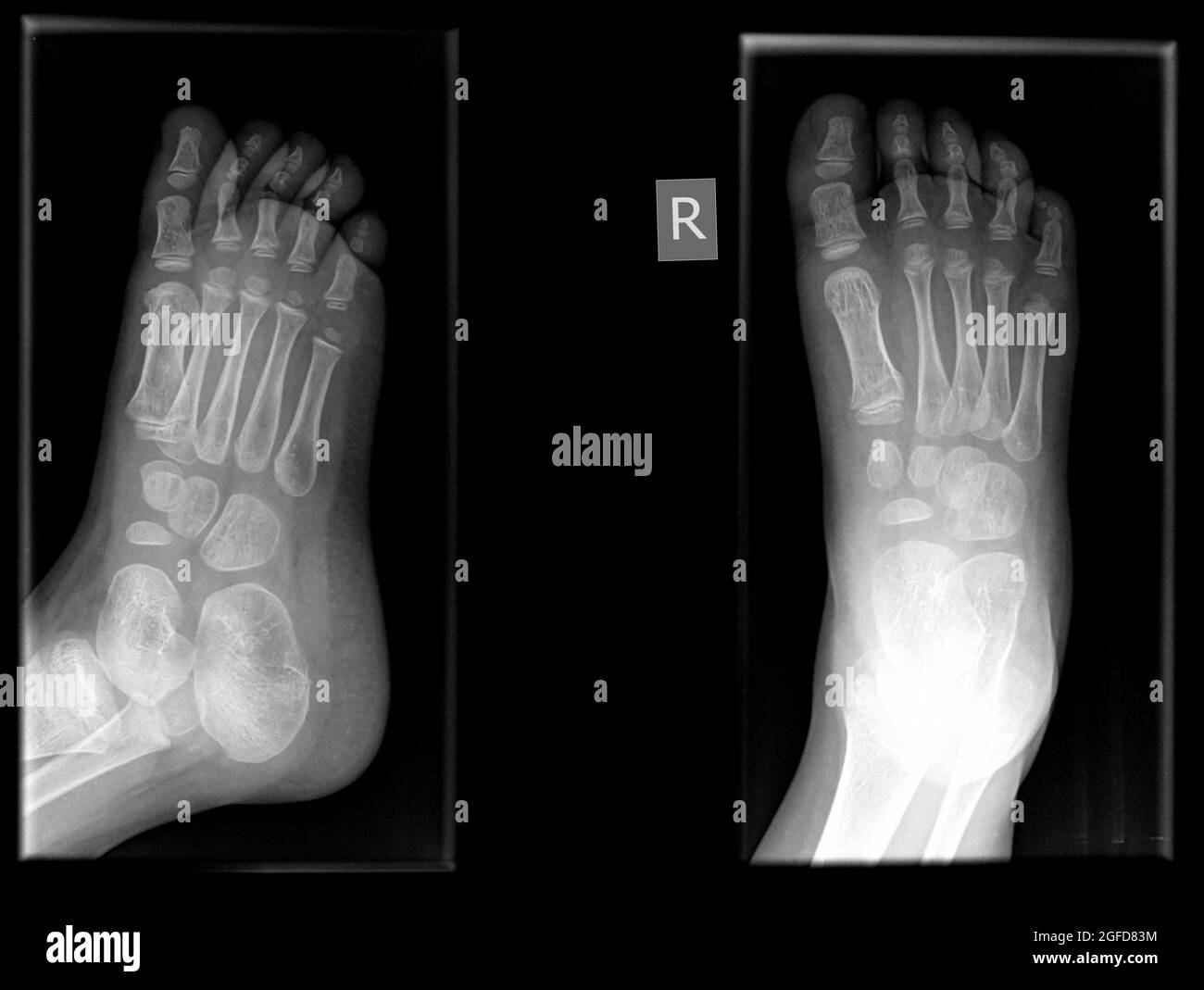
Radiografía del pie fotografías e imágenes de alta resolución Alamy
Cobey described a posterior view of the foot, modifying the Harris-Beath calcaneal axial view such that distortion was minimized (by directing the x-ray beam perpendicular to the image receptor). The patient stood on a radiolucent platform, and a 14 × 17-inch image receptor was positioned anterior to the patient and extending partially below the platform such that it was tilted 15-20° from.

Lower Extremity Os Foot & Ankle Orthobullets
The purpose of this article is to discuss the radiographic assessment of pediatric foot alignment. Clinical scenarios are included to orient the learner to the evaluation of pedi-atric foot alignment. Abnormalities discussed include, but are not limited to, talipes equinovarus (congenital clubfoot), planovalgus, and vertical talus.

Pedis X Ray Anatomy Radiology Radiographic Stock Photo 1459919159
It is useful in diagnosing fractures, soft tissue effusions, joint space abnormalities and localizing foreign bodies in pediatric patients. Patient position the affected leg is externally rotated until the lateral aspect of the foot is resting on the image receptor affected foot is slightly dorsiflexed Technical factors lateral projection

Pedis X Ray Anatomy Radiology Radiographic 스톡 사진 1459919177 Shutterstock
Adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD) is a common disorder that typically affects middle-aged and elderly women, resulting in foot pain, malalignment, and loss of function. The disorder is initiated most commonly by degeneration of the posterior tibialis tendon (PTT), which normally functions to maintain the talonavicular joint at the apex of the three arches of the foot. PTT degeneration.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13588/Dorsalis_pedis_artery.png)
Dorsalis pedis artery Anatomy, branches, supply Kenhub
First cuneiform (medial) Medial sesamoid. Lateral sesamoid. Shaft of second metatarsal. Neck of third metatarsal. Head of fourth metatarsal. Metatarsophalangeal joint. Proximal phalanx. Middle phalanx.

Understanding the foot's functional anatomy in physiological and
Introduction Infants and children undergo imaging studies to evaluate a wide variety of congenital and acquired disorders. The first imaging study is conventional radiographs; sometimes they are performed with the need for additional imaging which is guided by the plain film findings and clinical presentation.

Vascular Imaging of the Foot The First Step toward Endovascular
Normal chest x ray. Radiological anatomy is where your human anatomy knowledge meets clinical practice. It gathers several non-invasive methods for visualizing the inner body structures. The most frequently used imaging modalities are radiography (X-ray), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).X-ray and CT require the use of ionizing radiation while MRI uses a magnetic.